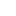Phantom Fighter Jet Lapel Pin
Wear this Phantom Aircraft Pin with pride at any time of the year not just Remembrance Week.
Made with High quality metals and enamels
2 x Rear metal butterfly pin fasteners..
Size: 35mm
Worldwide postage will be added at checkout for your country destination. Using the current Royal Mail Standard Delivery Tariffs. Tracked & Signed options are available.
Why not purchase a pack of Spring Loaded Chrome Pin Savers, never lose another lapel pin. Very secure.
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II[N 1] is a tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed for the United States Navy by McDonnell Aircraft.[2] It first entered service in 1960 with the U.S. Navy. Proving highly adaptable, it was also adopted by the U.S. Marine Corps and the U.S. Air Force, and by the mid-1960s had become a major part of their air arms.[3]
The Phantom is a large fighter with a top speed of over Mach 2.2. It can carry more than 18,000 pounds (8,400 kg) of weapons on nine external hardpoints, including air-to-air missiles, air-to-ground missiles, and various bombs. The F-4, like other interceptors of its time, was designed without an internal cannon. Later models incorporated an M61 Vulcan rotary cannon. Beginning in 1959, it set 15 world records for in-flight performance,[4] including an absolute speed record, and an absolute altitude record.[5]
The F-4 was used extensively during the Vietnam War. It served as the principal air superiority fighter for the U.S. Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps and became important in the ground-attack and aerial reconnaissance roles late in the war. During the Vietnam War, one U.S. Air Force pilot, two weapon systems officers (WSOs),[6] one U.S. Navy pilot and one radar intercept officer (RIO) became aces by achieving five aerial kills against enemy fighter aircraft.[7] The F-4 continued to form a major part of U.S. military air power throughout the 1970s and 1980s, being gradually replaced by more modern aircraft such as the F-15 Eagleand F-16 Fighting Falcon in the U.S. Air Force, the F-14 Tomcat in the U.S. Navy, and the F/A-18 Hornet in the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps.
The F-4 Phantom II remained in use by the U.S. in the reconnaissance and Wild Weasel (Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses) roles in the 1991 Gulf War, finally leaving service in 1996.[8][9] It was also the only aircraft used by both U.S. flight demonstration teams: the USAF Thunderbirds (F-4E) and the US Navy Blue Angels (F-4J).[3][10][11] The F-4 was also operated by the armed forces of 11 other nations. Israeli Phantoms saw extensive combat in several Arab–Israeli conflicts, while Iran used its large fleet of Phantoms, acquired before the fall of the Shah, in the Iran–Iraq War. Phantom production ran from 1958 to 1981, with a total of 5,195 built, making it the most produced American supersonic military aircraft.[3][12] As of 2018, 60 years after its first flight, the F-4 remains in service with Iran, Japan, South Korea, Greece and Turkey. The aircraft has most recently been in service against the Islamic State group in the Middle East.